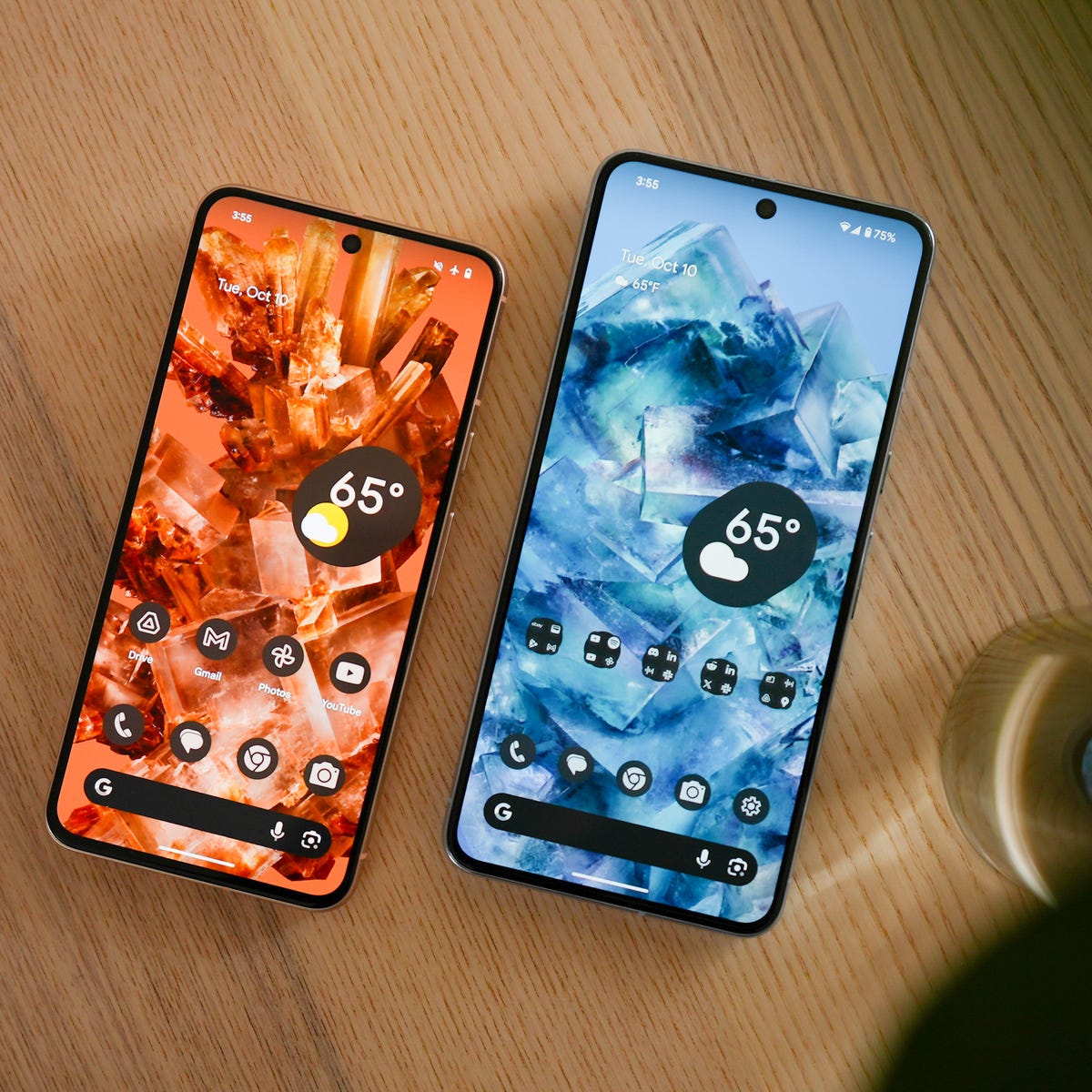
Display: High-resolution OLED or AMOLED display with a high refresh rate (typically 90Hz or 120Hz) for smooth scrolling and animations.
Camera: Multiple rear cameras with advanced computational photography capabilities, including features like Night Sight for low-light photography, portrait mode, and various AI enhancements for better image quality.
Processor: Latest-generation Qualcomm Snapdragon or Google Tensor processor for improved performance and energy efficiency.
Battery: Large battery capacity with fast charging capabilities and possibly wireless charging support.
Operating System: Running the latest version of Android with exclusive features and optimizations tailored for the Pixel lineup.
Connectivity: Support for 5G connectivity, Wi-Fi 6E, Bluetooth 5.2, NFC, and other standard wireless protocols.
Design: Premium build quality with glass or metal construction, possibly with water and dust resistance (IP68 rating).
Security: Advanced biometric authentication methods like face unlock and in-display fingerprint sensors.
Software Features: Exclusive software features such as Google Assistant enhancements, Pixel-exclusive apps, and software updates directly from Google for timely security patches and new features.
Additional Features: Stereo speakers, Always-on Display, customizable user interface, and possibly improved gaming performance with dedicated optimizations.