The European Union has recently introduced a new economy plan aimed at transforming the region's economic landscape. The plan focuses on several key areas, including digitalization, sustainability, competitiveness, and social cohesion. The plan aims to strengthen the European economy and make it more resilient to future challenges.
This essay will provide a detailed analysis of the EU's new economy plan. It will examine the plan's objectives, strategies, and expected outcomes. The essay will also discuss the potential challenges and risks associated with the plan's implementation.
Objectives of the EU's New Economy Plan
The EU's new economy plan has several objectives, which can be broadly categorized into three main areas: digitalization, sustainability, and competitiveness.
Digitalization
One of the primary objectives of the EU's new economy plan is to promote digitalization across the region. This includes developing a comprehensive digital strategy that will enable the EU to compete with other regions such as China and the United States.
The plan aims to achieve this objective through several strategies, including investing in digital infrastructure, promoting digital innovation, and improving digital skills. The EU plans to invest in digital infrastructure by expanding high-speed internet and 5G networks across the region. The plan also aims to promote digital innovation by increasing investment in research and development and supporting start-ups and small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
To improve digital skills, the EU plans to provide training and upskilling programs for workers, particularly those in industries that are being disrupted by automation and digitalization. The plan also aims to develop a framework for the ethical and responsible use of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain.
Sustainability
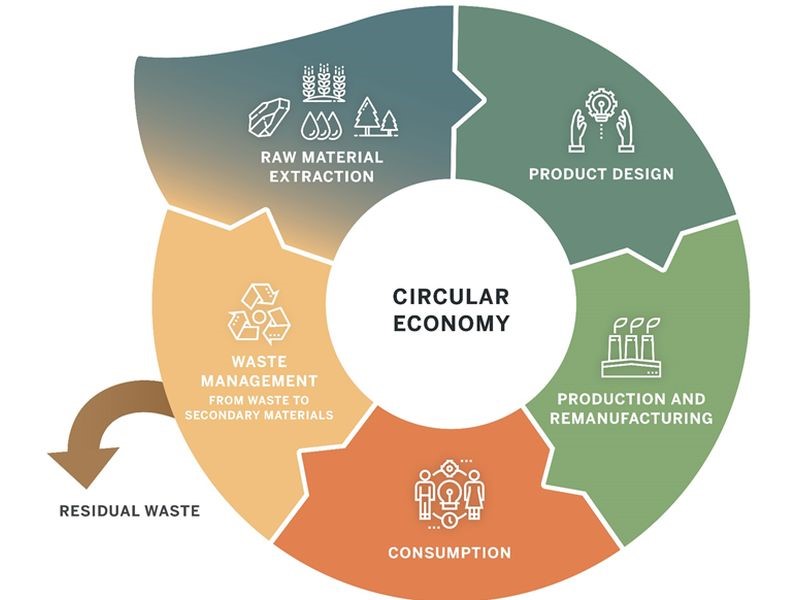
Another key objective of the EU's new economy plan is to promote sustainability across the region. This includes reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving resource efficiency, and promoting circular economy principles.
To achieve this objective, the EU plans to implement several strategies, including investing in clean energy, promoting sustainable mobility, and supporting circular economy initiatives. The plan aims to invest in clean energy by increasing the use of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power. The plan also aims to promote sustainable mobility by investing in public transportation and encouraging the use of electric vehicles.
To support circular economy initiatives, the EU plans to develop a comprehensive circular economy action plan that will promote the reuse, repair, and recycling of products and materials. The plan also aims to promote sustainable agriculture and reduce food waste.
Competitiveness
The third objective of the EU's new economy plan is to promote competitiveness across the region. This includes improving the business environment, promoting innovation, and strengthening the EU's industrial base.
To achieve this objective, the EU plans to implement several strategies, including simplifying regulations, reducing administrative burdens, and promoting entrepreneurship. The plan aims to promote innovation by increasing investment in research and development and supporting the development of new technologies.
The plan also aims to strengthen the EU's industrial base by promoting strategic sectors such as the automotive and aerospace industries. The plan aims to support the development of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) by providing access to financing and supporting entrepreneurship.
Strategies of the EU's New Economy Plan
To achieve its objectives, the EU's new economy plan includes several strategies, which are discussed below.
Digitalization
Investing in digital infrastructure: The EU plans to invest in digital infrastructure by expanding high-speed internet and 5G networks across the region. The plan aims to ensure that all EU citizens have access to affordable, high-quality digital services.
Promoting digital innovation: The EU plans to promote digital innovation by increasing investment in research and development and supporting start-ups and SMEs. The plan also aims to create a favorable environment for digital innovation by promoting entrepreneurship and reducing administrative burdens.
Improving digital skills: The EU plans to improve digital skills by providing training and upskilling programs